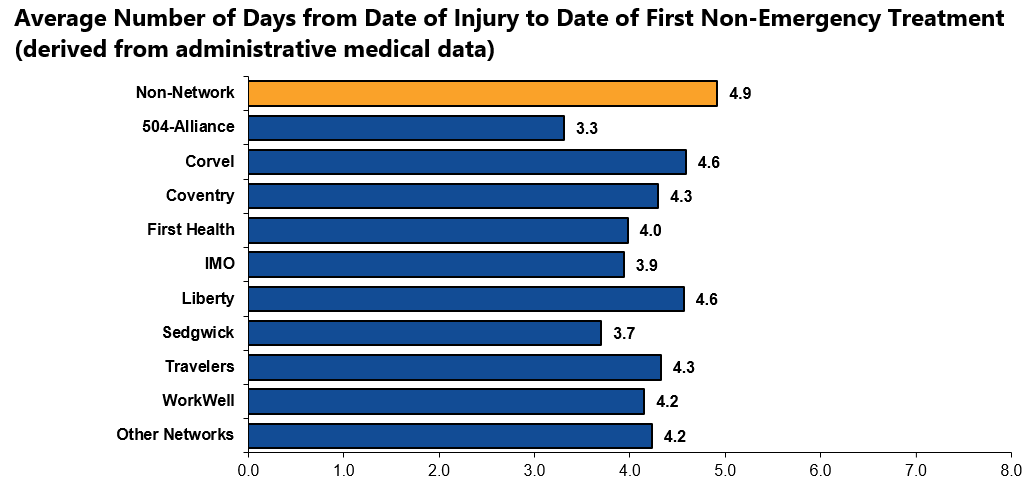
Key findings
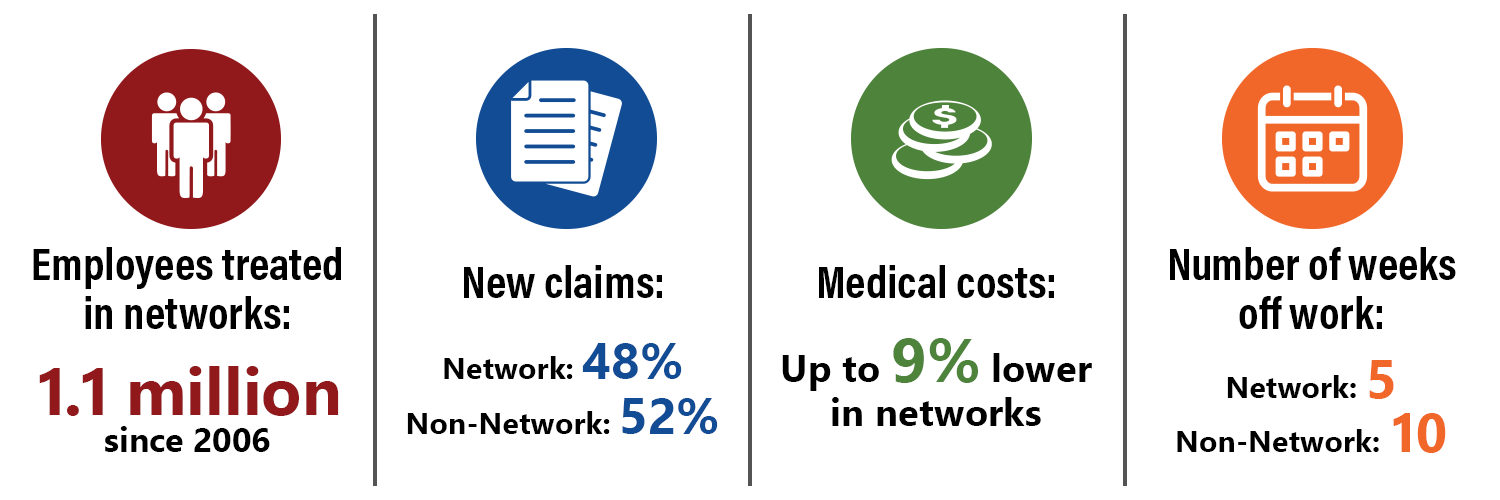
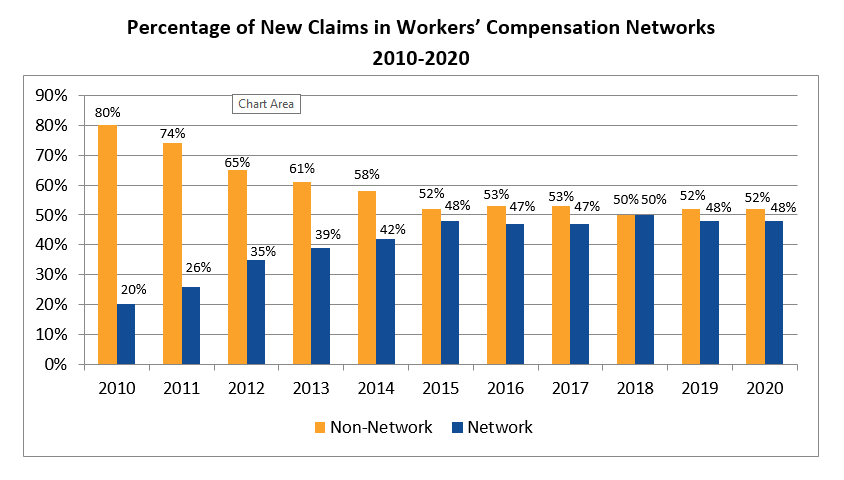
48 percent of all new workers’ compensation claims in 2020 have been treated in networks, up from 28 percent in 2010.
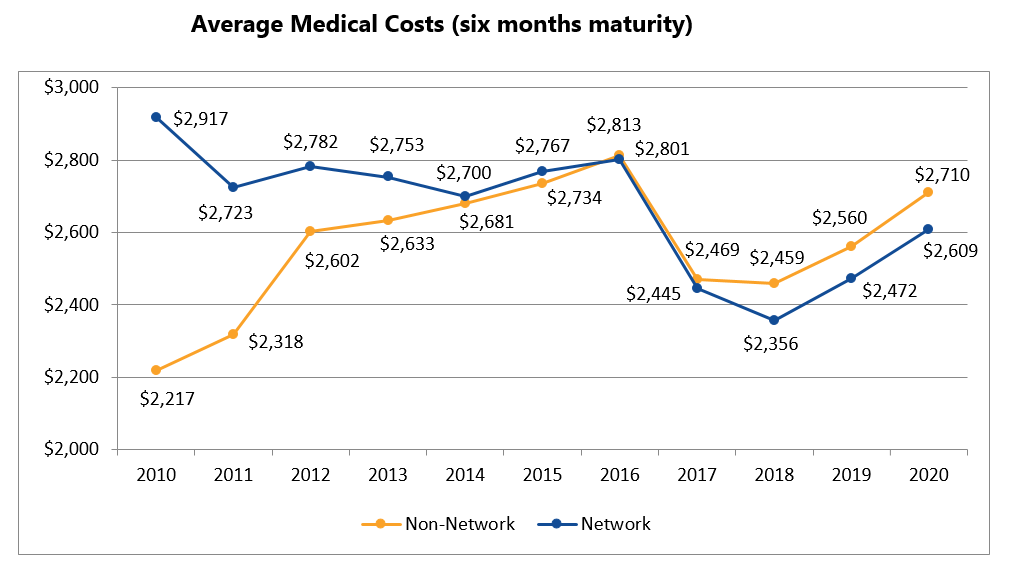
Overall, medical costs in networks still outperform those in non-network. In 2020, network medical costs were about 9 percent lower per claim at 18 months post-injury compared with non-network claims.
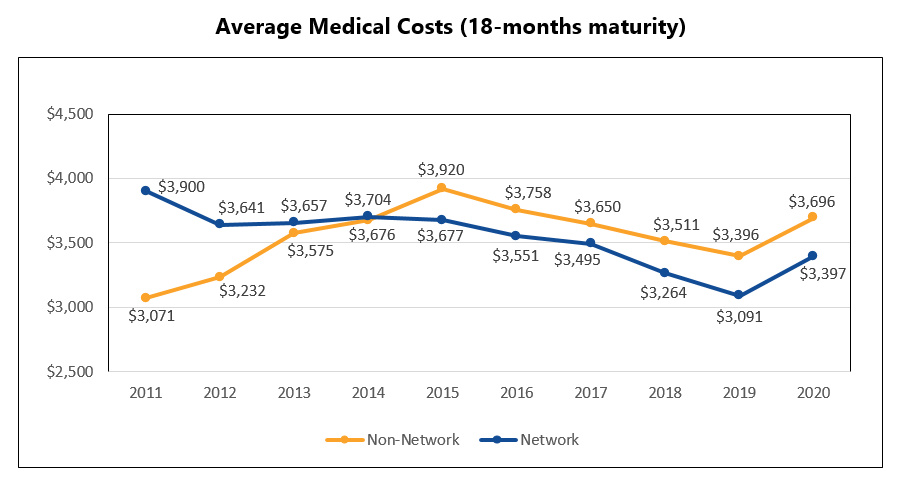
The medical cost gap widened between network and non-network claims at 18 months post-injury (using claims from the previous report card). Network medical costs were about 9 percent lower per claim at 18 months post-injury compared with non-network claims.
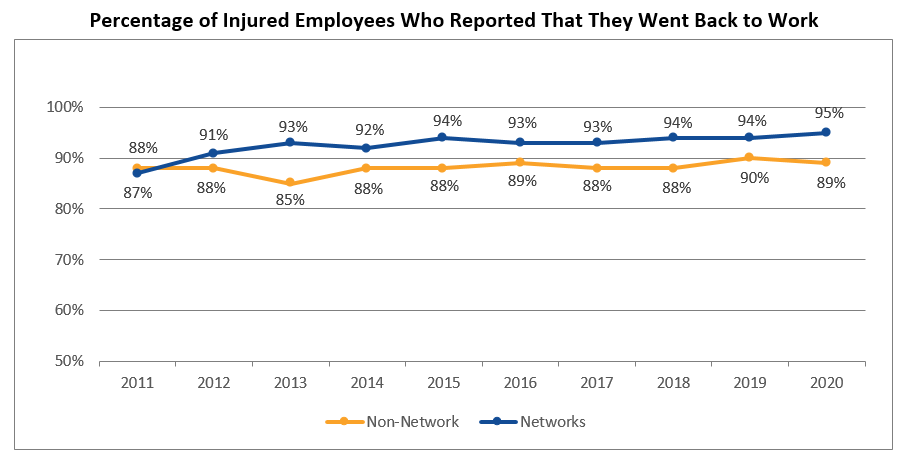
The percentage of network injured employees who went back to work after their injury increased to 95 percent in 2020, an eight percent increase since 2011. The return-to-work rate for non-network injured employees declined slightly to 89 percent for the same timeframe.
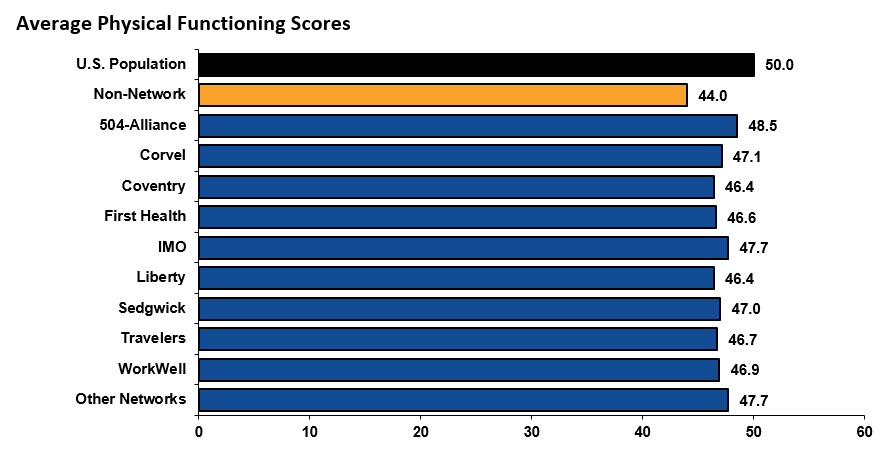
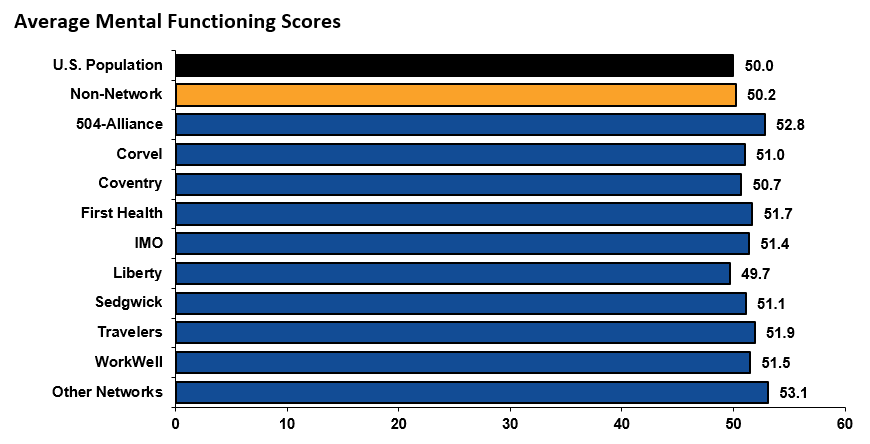
Physical functioning measures a person’s ability to do everyday tasks. Mental functioning measures a person’s ability to think and reason. All networks had higher physical functioning scores among their injured employees than non-network. Most network patients had better or equal mental functioning scores as well. Both of these scores among network injured employees have consistently been higher than those of non-network injured employees and the U.S. population since 2012.